Digital twin technology changes how we interact with the physical world. It creates virtual copies of real objects. These copies allow for real-time tracking and improvement. Many fields benefit from this innovative technology. For example, industries like manufacturing and healthcare are inspired by these advancements. Want to understand how it works and why it matters? Keep reading!
Listen to Our Podcast on Digital Twin Technology: Bridging the Physical and Digital Worlds:
What is Digital Twin Technology?
A digital twin is a virtual copy or a simulation of a physical object or a system. This can be said to be true to real-life models to a very large extent. This digital model is integral and concerns the physical entity from its inception to its disposal. It can always be refreshed with its contents showing in the real-time style to depict the current state in the best way possible. Users apply IoT, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence (AI), among other related trends. Digital twins provide an understanding of performance, future issues, and opportunities for enhancements.
What are the Components of Digital Twins?
Digital twins are popular and valuable tools used in multiple sectors and industries. They cause the making of imitation digital models of actual objects. When you are aware of the main components of digital twins, the idea can provide insight into how it functions and how it is capable of being valuable. Here are the key elements:
1. Physical Entity
The physical entity is the subject of replication, the actual object or system that is being replicated. These could be machines, structures, cars, or even complicated infrastructures such as dams, bridges, etc. For instance, a digital twin wind turbine accurately describes a real-world wind turbine. It enables monitoring and analyzing performance.
2. Digital Model
The digital model acts as the virtual counterpart to the physical entity. They replicate the qualities as well as activities of the original actual object. This model can be in two dimensions or three dimensions. Also, it may contain data sets that characterize the object’s functioning under certain conditions.
3. Data Sources
Practical data sources that can be necessary for creating a digital twin are important. These devices and sensors obtain physical information on the entity at real time. They capture data about temperature, pressure and its working condition. Into this, the data continuously feeds the digital model. It helps to achieve that the model represents the organization in the state of its physical element.
4. Analytics Engine
Information derived from the physical entity is analyzed by an analytics engine. It employs tools and algorithms when processing the information. This one gives information that could be used to make decisions. For example, predictive analytics provides an approximate of when an equipment is going to require maintenance thus cutting on the time it takes to be worked on.
5. User Interface
From a user perspective, there is a user interface for a number of inputs in its digital twin. It also may contain components such as dashboards and visualizations. These tools facilitate present of data in a manner easy to comprehend. It is possible to control key parameters and be alerted about their status, as well as make decisions based on actual information.
Additional Components
While these five components are fundamental, additional aspects enhance the functionality of digital twins:
6. Integration with IoT
Typically, digital twins are connected with the Internet of Things (IoT) technology. It is essential to integrate various tools to collect large amounts of information from various sources to obtain a complete understanding of the work carried out in an enterprise. It also improves the ability to monitor in real-time.
7. Simulation Capabilities
Not all digital twins can simulate. These capabilities enable the users to prototype scenarios that will not have an impact on the physical entity. For instance, engineers are able to have various tests on operational conditions. Plus, they being able to see how change could affect performance.
8. Feedback Loop
There is a feedback loop when the information generated by the analytics engine results in changes within the physical entity or its processes. This brings about the cycle which enhances performance over a period.
Digital twin technology creates a strong connection between the physical and digital worlds. It helps businesses improve efficiency and make informed decisions.
Types of Digital Twins
Digital twins come in different types. Each type serves a unique purpose. Understanding these types helps organizations select the right digital twin for their needs. Here are the main types:
1. Component Twins
Component twins represent individual parts within a larger system. They focus on the smallest units of functionality. For example, a component twin could stand for a single gear in a machine. Engineers can model this part to analyze its performance under various conditions. This analysis helps identify potential weaknesses. Component twins are crucial for industries where precision and reliability are essential, like aerospace and automotive.
2. Asset Twins
Asset twins represent assets made up of multiple components. They analyze how these components work together. For instance, an asset twin of a wind turbine includes its blades, generators, and control systems. Operators can use an asset twin to monitor the turbine’s overall performance. They can predict maintenance needs and optimize energy output. This comprehensive view helps organizations improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
3. System or Unit Twins
System or unit twins model entire systems or units. They provide insights into how different assets integrate and function together. For example, a system twin might represent a complete manufacturing line. This model shows how machines, workers, and processes interact. Companies can optimize workflows and identify bottlenecks using this type of twin. By simulating various scenarios, businesses can make informed decisions about process improvements.
4. Process Twins
Process twins represent entire production processes or facilities. They help organizations optimize overall operations and improve efficiency. For instance, a process twin could model a factory’s complete production line, from raw material input to finished product output. This broad view enables organizations to analyze performance metrics and streamline operations. It also helps reduce waste. With real-time data integration, companies can swiftly respond to changes in demand or production issues.
For an in-depth exploration, read our article on Understanding Component and Asset Twins in Digital Twin Technology.
Applications Across Industries

Digital twin technology impacts many industries. It provides solutions that enhance efficiency and decision-making. Here are some key areas where digital twins are making a difference:
1. Manufacturing
Digital twins optimize production processes in manufacturing. They allow manufacturers to simulate different scenarios. This helps them identify inefficiencies before making changes on the factory floor. For example, a digital twin can represent a whole production line. Managers can test adjustments without disrupting real operations. This method saves time and cuts costs related to trial-and-error methods.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, digital twins model patients using their medical history and real-time health data. This approach helps doctors tailor treatments for individual needs. For instance, a digital twin can simulate how a patient might respond to a specific medication. This allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment plans. Additionally, hospitals can create digital twins of their facilities. This improves operational efficiency and resource management.
3. Automotive
Automakers use digital twins to design vehicles. They can test performance under various conditions without needing physical prototypes. This speeds up development and lowers costs. By creating a digital twin of a car, engineers analyze how different parts interact. They can optimize designs for safety and efficiency. Furthermore, digital twins assist in predictive maintenance. They help manufacturers predict when parts need replacements before they fail.
4. Smart Cities
Digital twins help in urban planning. City planners can create models that visualize traffic patterns, energy use, and environmental impacts. For example, a city might develop a digital twin to simulate the effects of new public transportation routes. Changes in zoning laws can also be tested. This allows planners to make data-driven decisions. They can improve infrastructure and enhance residents’ quality of life.
5. Energy Management
In the energy sector, digital twins monitor power plants and renewable energy sources. They track the performance of wind turbines and solar panels. By analyzing real-time data, companies optimize energy production and reduce downtime. For example, a digital twin of a wind farm can predict when maintenance is necessary. It uses historical performance data and current conditions to make these predictions.
6. Supply Chain Optimization
Digital twins play a crucial role in supply chain optimization. They provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipping times, and demand forecasts. Companies can create a digital twin of their entire supply chain. This helps identify bottlenecks and improve logistics efficiency. If a delay occurs in one part of the supply chain, managers can quickly assess alternatives to minimize disruption.
7. Construction
In construction, digital twins help firms understand building performance in real-time. They collect data from sensors embedded in structures. This data monitors conditions like temperature, humidity, and occupancy levels. The information allows for better maintenance planning and energy management after construction.
Discover more in our post on Digital Twins in Manufacturing: Revolutionizing Production Processes.
Benefits of Implementing Digital Twins

Digital twins are virtual models that represent physical objects, systems, or processes. They offer valuable insights and can greatly improve operations in various industries. Here are the main benefits of implementing digital twins:
1. Enhanced Decision-Making
Digital twins help businesses make better decisions using real-time data and simulations. Companies can analyze how a system performs in different conditions. This analysis allows them to quickly identify the best course of action. As a result, they can make informed choices that increase efficiency and cut costs.
2. Predictive Maintenance
One major advantage of digital twins is their ability to predict maintenance needs. They continuously monitor equipment and analyze performance data. Businesses can then schedule maintenance before a failure occurs. This proactive approach reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of assets.
3. Improved Product Development
Digital twins enable companies to test and refine products in a virtual setting before production. This testing helps them spot potential issues early, which saves time and money. By simulating various scenarios, teams can optimize designs and improve product quality.
4. Increased Operational Efficiency
Using digital twins allows organizations to streamline their operations. They can analyze workflows and identify bottlenecks. Based on this data, they can implement improvements. This process leads to more efficient operations and better resource management.
5. Real-Time Monitoring
Digital twins provide real-time visibility into how systems and processes work. Businesses can continuously monitor performance and detect any anomalies. This quick response helps maintain optimal performance levels.
6. Cost Savings
Implementing digital twins can lead to significant cost savings over time. Improved maintenance practices and better product development lead to lower operational costs. Organizations can also reduce waste along the way.
7. Better Customer Experiences
Digital twins help businesses understand customer behavior and preferences. Companies can better tailor their offerings by analyzing how customers interact with products or services. This approach leads to higher satisfaction rates among customers.
8. Support for Sustainability Goals
Digital twins can simulate different scenarios to assess the environmental impact of operations. Companies can discover ways to reduce waste and lower emissions. This capability helps them improve energy efficiency and supports their sustainability initiatives.
9. Facilitation of Remote Work
Digital twins enable teams to monitor and manage systems remotely. This feature is increasingly valuable in today’s work environment. Remote operations are becoming more common, and teams can collaborate effectively while keeping track of critical operations.
Learn how digital twins facilitate Predictive Maintenance with Digital Twins: Reducing Downtime and Costs.
Challenges and Considerations
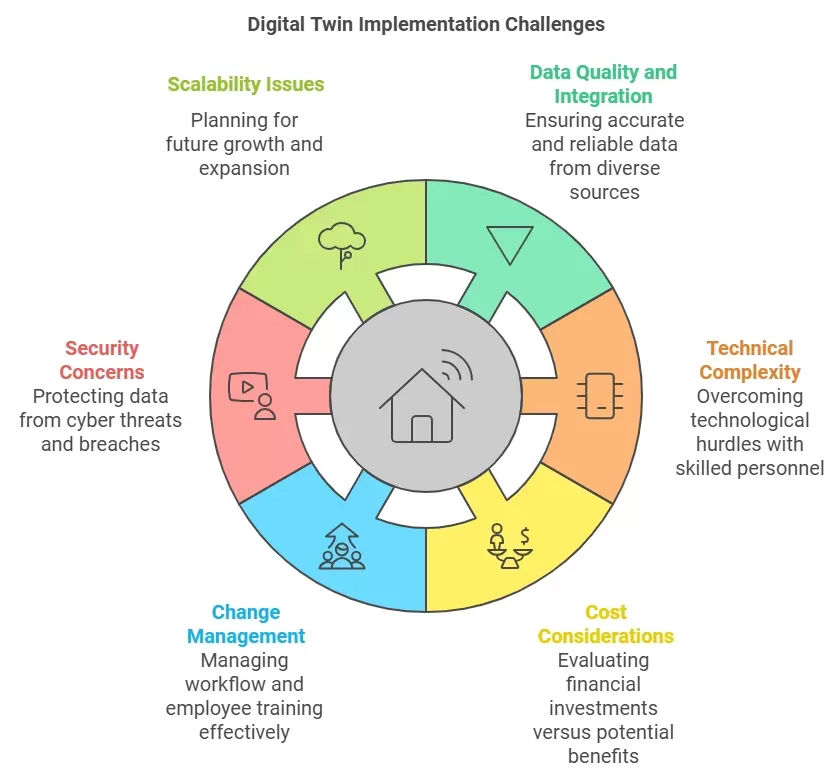
Implementing digital twins can bring many benefits. However, organizations face several challenges and considerations. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
1. Data Quality and Integration
One major challenge is ensuring data accuracy and reliability. Poor data quality can result in incorrect simulations and decisions. Integrating data from various sources can also be complex. Therefore, organizations need to set clear processes for data collection and management. This step ensures consistency in data use.
2. Technical Complexity
Creating a digital twin requires advanced technology. This includes sensors, software, and analytics tools. Organizations may encounter technical difficulties while setting up these systems. It is important to have skilled personnel who understand the technology and the specific processes being modeled.
3. Cost Considerations
The initial investment in developing a digital twin can be significant. This investment covers technology, training, and ongoing maintenance. Organizations must carefully evaluate whether the potential benefits justify these costs. They should also consider any budget constraints they may have.
4. Change Management
Introducing a digital twin often requires workflow and process changes. Employees may need training to use new tools and practices. Additionally, resistance to change can hinder successful implementation. To address this, organizations should focus on good communication and provide support during this transition.
5. Security Concerns
Increased connectivity raises the risk of cyber threats. Therefore, protecting the data used in digital twins is crucial. Organizations need to implement strong security measures to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. This approach safeguards sensitive information.
6. Scalability Issues
As organizations grow, their digital twins must scale as well. This scaling can be challenging if the initial design does not account for future expansion. Therefore, planning for scalability from the beginning can help avoid complications later on.
Read about strategies to Overcome Data Integration Challenges in Digital Twin Implementation.
Future Trends in Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology is changing how businesses operate in many industries. This technology evolves quickly. Several trends will shape its future applications and effectiveness. Here are some key trends to watch:
· Increased Use of IoT Integration
IoT devices are crucial for digital twins. They connect physical objects to the internet. These devices collect real-time data to create accurate digital replicas. This connection helps businesses monitor and manage their assets better. As a result, it leads to improved efficiency and less downtime.
· Enhanced Data Analytics
Digital twins generate a lot of data. Businesses will rely on advanced data analytics tools to make sense of this information. They will use machine learning and artificial intelligence for analysis. These tools will provide deeper insights into performance. Moreover, they will enable predictive maintenance. Companies can then anticipate issues before they arise, saving valuable time and resources.
· Expansion Across Industries
Digital twin technology is growing beyond manufacturing and automotive sectors. Its applications are spreading to industries like healthcare, construction, and smart cities. For instance, in healthcare, digital twins can model patient health data. This modeling helps personalize treatment plans. In construction, these technologies can simulate building performance to optimize energy use.
· Real-Time Monitoring and Simulation
Future digital twins will focus on real-time monitoring and simulation capabilities. Businesses will track the performance of their assets continuously. They can also simulate different scenarios to see how changes might impact operations. For example, manufacturers can test production line changes in the digital realm before applying them in real life. This approach reduces risks associated with new processes.
· Improved User Interfaces
As digital twin technology advances, user interfaces will become more intuitive and user-friendly. Enhanced visualization tools will enable users to interact with digital twins more effectively. This improvement makes it easier to understand complex data. Consequently, users can make informed decisions quickly.
· Greater Focus on Sustainability
With growing awareness of environmental issues, digital twins will help promote sustainability. They allow organizations to monitor their resource usage and spot areas for improvement. For instance, a digital twin of a factory can analyze energy consumption patterns. It can then suggest ways to reduce waste, which benefits both the environment and the organization.
· Collaboration Across Teams
Digital twins encourage collaboration among different teams within an organization. They provide a shared virtual model that helps teams work together more effectively on projects. This cooperation leads to better outcomes. This collaborative approach is especially important for complex projects like urban planning or large-scale manufacturing.
Organizations can use digital twin technology to connect the physical and digital worlds. This connection improves efficiency, boosts innovation, and enhances competitiveness.
Stay informed with our insights on The Future of Digital Twin Technology: Emerging Trends and Innovations.
Final Words
Digital twin technology is changing how industries monitor, simulate, and optimize their operations. Organizations create accurate virtual replicas of physical entities. These replicas provide real-time insights and help in predicting potential issues. This leads to better decision-making processes. As this technology evolves, it will integrate with advanced analytics, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). This integration will further broaden its applications. Ultimately, these developments will drive innovation and improve efficiency across various sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a digital twin?
A digital twin is a virtual model of a physical object or system. It tracks the real-world item in real-time. Sensors and devices provide data to show how the item behaves and performs.
2. How does a digital twin differ from a simulation?
Digital twins and simulations create virtual models, but they differ in key ways. Digital twins receive real-time updates from their physical counterparts. This feature allows for ongoing monitoring. In contrast, simulations use fixed models for specific situations without real-time data.
3. What industries benefit from digital twin technology?
Many industries benefit from digital twin technology. Manufacturing, healthcare, urban planning, and energy sectors use it effectively. This technology helps them work more efficiently, predict maintenance needs, and optimize operations.
4. What are the challenges in implementing digital twins?
Several challenges come with implementing digital twins. These include managing data from various sources, ensuring data security, and expanding the technology across large systems. Companies must carefully plan and invest in the right tools to overcome these hurdles.
5. How do digital twins contribute to predictive maintenance?
Digital twins track the condition and performance of physical assets. They can detect potential failures early. This capability allows teams to perform proactive maintenance, which reduces downtime.
6. What is the future outlook for digital twin technology?
The future of digital twin technology looks promising. We expect advancements in AI and growth in new industries. Additionally, improvements in real-time data processing will lead to more advanced and widespread applications of digital twins.