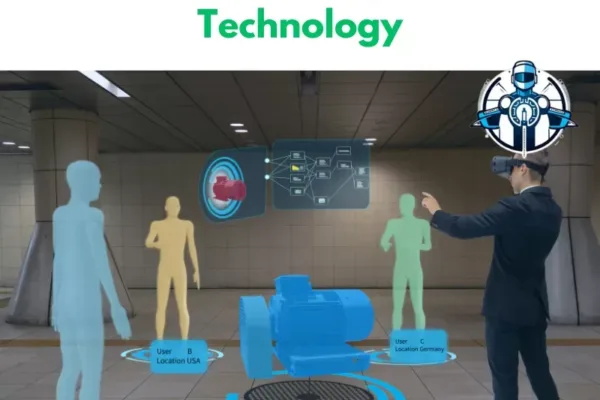
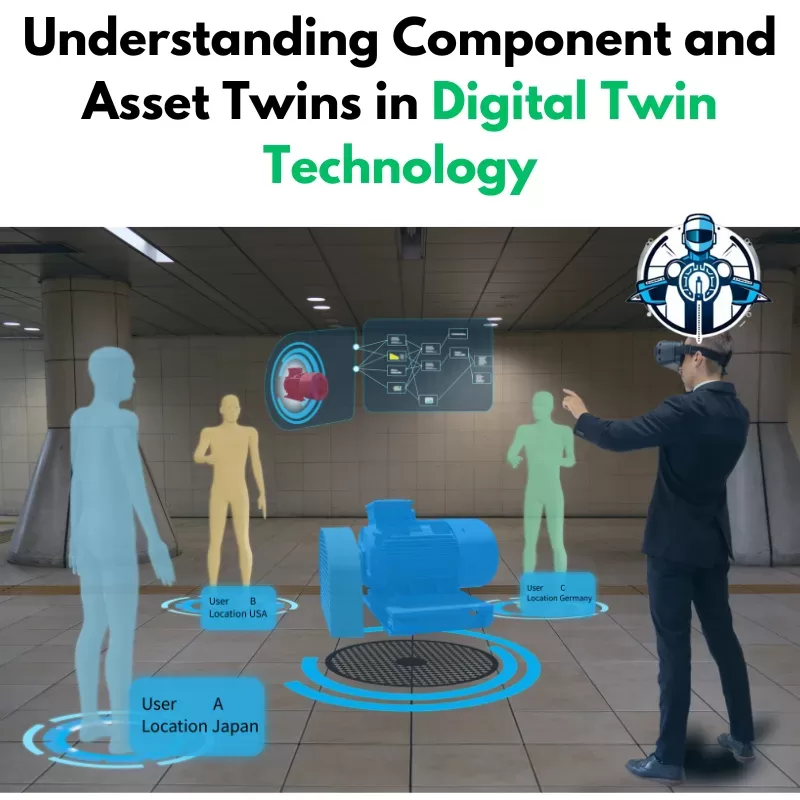
Component twins and asset twins are two important components of digital twin technology. We use them to simulate and solve problems of physical models. There are a few things that must be distinguished between these twins. Knowledge of such use makes it easier to maximize benefits of this technology.
Listen to Our Podcast on Component and Asset Twins in Digital Twin Technology:
Component Twins: The Basics
A component twin stands for a part of a system or a specific subpart. This could be a motor, a sensor, or a valve. Such digital versions enable organizations to monitor each part’s performance. They also enable teams to see possible failures in advance. For these reasons, organizations are able to optimize the steps for particular parts.
Asset Twins: Integrating Components
A component twin aggregates other component twins together to work as one asset in the twin system. For example, a wind turbine is a system that has a rotor, gearbox, and generator. All of these are component twin separations, to be specific. Altogether, they generate the asset twin of the whole turbine to create a cognizant and perceptive copy of the physical asset’s characteristics and behaviors. Finally, asset twins enable us to study the nature of learning between these parts. They afford an opportunity for an evaluation of the performance of the system and its requirements for maintenance.
Key Differences Between Component and Asset Twins

Both component and asset twins play vital roles in digital twin technology, but they focus on different aspects:
- Scope: Component twins examine individual parts. In contrast, asset twins cover the entire system of components.
- Data Granularity: Component twins deliver detailed information about specific parts. Asset twins, on the other hand, give a broader view of how the entire asset performs.
- Application: We use component twins for detailed analysis and optimization of single parts. Conversely, asset twins help us evaluate and enhance the performance of the whole asset.
Applications Across Industries
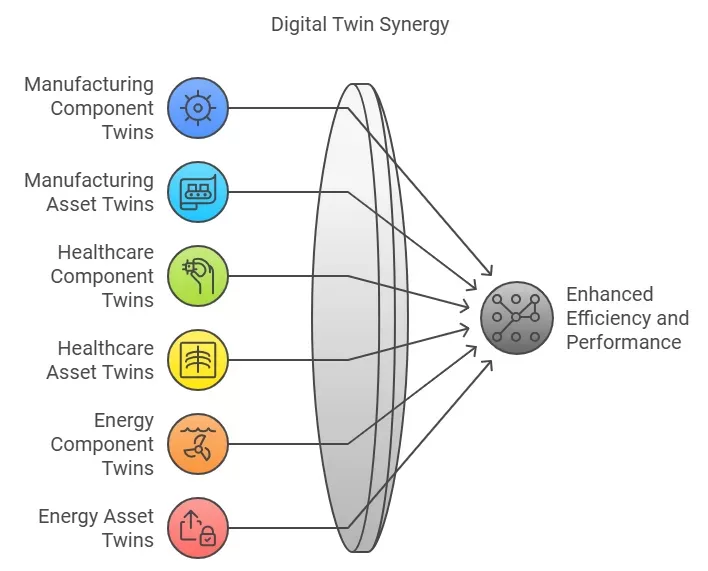
The use of component and asset twins varies by industry.
· Manufacturing:
Component twins monitor machine parts. They help with maintenance and reduce downtime. Asset twins oversee entire production lines. This leads to improved efficiency.
· Healthcare:
Component twins model medical devices. They ensure these devices work properly. Asset twins represent complex equipment, such as MRI machines. They aid in thorough diagnostics.
· Energy Sector:
Component twins track parts of power generation equipment. Meanwhile, asset twins manage overall system performance, including turbines and grids. This management ensures optimal operation.
Benefits of Using Component and Asset Twins

Using component and asset twins in operations offers several clear benefits.
- Better Monitoring: Component twins provide real-time data. This data helps us detect problems immediately.
- Predictive Maintenance: Asset twins help us predict possible failures. This capability reduces unexpected downtime.
- Improved Performance: We can analyze how components interact with asset twins. This analysis allows us to enhance system efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing component and asset twins offers benefits. However, it also presents challenges:
- Data Integration: Merging data from different components into one asset twin can be tricky.
- Scalability: You need careful planning and significant resources to expand digital twins across large systems.
- Security: You must protect data and ensure privacy. This is especially important in healthcare.
Future Outlook

Digital twin technology is evolving. It is becoming more advanced due to:
- Integration with AI: This integration will enhance predictive abilities and automation.
- Real-Time Analytics: Real-time analytics will improve response times and boost decision-making.
- Cross-Industry Applications: Digital twins are now entering new fields such as agriculture and retail.
However, understanding and effectively implementing component and asset twins is crucial. It helps unlock the full potential of digital twin technology. This leads to better efficiency, increased innovation, and more competitiveness in various industries.
Final Words
So, now you understand the difference between component twins and asset twins for effective use of digital twin technology. Component twins focus on individual parts. They allow for better monitoring and maintenance of those parts. On the other hand, asset twins provide an overall view of entire systems. This view helps optimize system performance.
When we combine both types of twins, we can achieve greater efficiency. This combination also supports predictive maintenance. As a result, we can make better decisions in various fields. However, understanding these differences can lead to significant improvements in how we manage technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a component twin?
A component twin is a digital copy of a single part in a system. This part could be a motor or a sensor. It focuses on that part’s specific features and behaviors.
2. How does an asset twin differ from a component twin?
An asset twin shows how a group of component twins works together. It gives insights into how these parts interact. Additionally, it shows how well they perform together.
3. Why are component and asset twins important in digital twin technology?
These twins help us monitor systems closely. They allow us to predict when maintenance is needed. They also improve performance. This leads to more efficient operations and better decision-making.
4. Can component and asset twins be used together?
Yes, using both provides a detailed analysis. We can look at individual parts and the whole system. This approach leads to better management and optimization.
5. Which industries benefit from using component and asset twins?
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and energy greatly benefit from these twins. They help monitor equipment, foresee maintenance issues, and improve overall performance.