First came Robotic Process Automation or RPA. It operated with the help of software to do work that could be done mechanically, that is, which involved following a set of rules. Then came the automation through artificial intelligence. This enabled the machines to perform other tasks that would have needed the machine to think in some way. For instance, it provided the functionalities of intelligent document processing (IDP), communication analysis, and process assessment. Now, we encounter agentic automation. This is the current advance in automation technology.
But what does this really mean? Well, let’s break it down in simple terms.
Listen to our Podcast: Agentic Automation?
What is Agentic Automation?

Agentic automation is a new form of automation and represents a major advancement in automation technology. It employs some of the latest software agents that use tools such as large language models and generative AI. These agents can act independently. They are aware of their environment, they process information, propose questions that are significant for achievement of goals and develop plans to achieve the goals set without assistance of humans.
Discover the full potential of Agentic AI in Agentic AI Revolutionizing Technology.
Key Features:
- Independent Decision-Making: Agents can make choices without human input.
- Learning Ability: They can learn from experiences to improve over time.
- Adaptability: Agents can adjust to new situations and changes in their environment.
Learn how Agentic AI is transforming financial services in our blog Revolutionizing Financial Services with Agentic AI.
What do we mean by agentic automation, artificial intelligence automation, and RPA?
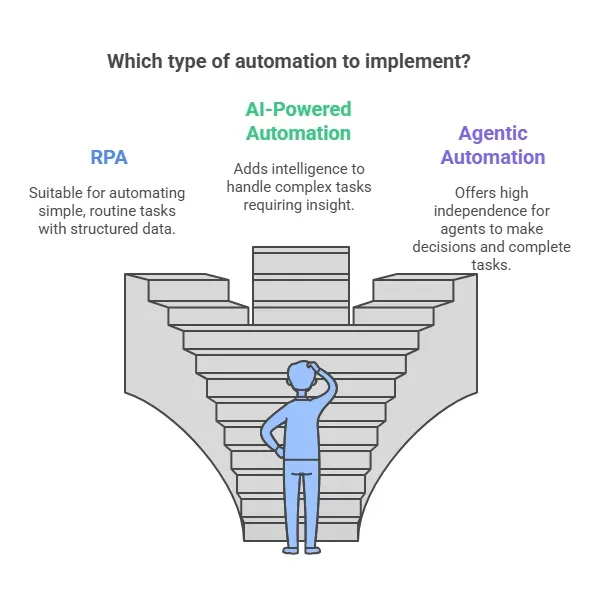
Here’s a clear and simple explanation of the differences between agentic automation, AI-powered automation, and RPA:
1. RPA (Robotic Process Automation):
RPA automates simple tasks. It deals with routine tasks, which have specific guidelines and involve structured data. For instance, RPA is ideal for use in activities such as data input and processing of invoices and such like. It also deals with these boring tasks. Therefore, human employment can be focused on the tasks that require imagination and decision-making skills of a human.
2. AI-Powered Automation:
This type of automation adds smart technology to RPA. It allows software robots to tackle more complicated tasks. These tasks may involve understanding information, pulling insights, and even reading emotions in text. Technologies like machine learning and natural language processing make this possible. Although this approach offers more flexibility, humans still need to oversee it to define the tasks properly.
3. Agentic Automation:
This is the most advanced type of automation. It uses Generative AI to give software agents a high level of independence. These agents can examine unstructured data, spot patterns, make decisions, and finish tasks without direct human control. For instance, a user may provide a general prompt. After this, the agent can figure out how to collect and analyze information from different sources to get the job done effectively.
However, RPA handles straightforward tasks. AI-powered automation adds cognitive abilities for more complex jobs. Finally, agentic automation lets software agents work on their own and make decisions independently.
What are some common applications of agentic automation?
Agentic automation is a new technology with many uses in different industries. Here are some common applications:
1. Banking and Financial Services:
Agents analyze market trends and evaluate investments. They create personalized financial plans. This allows advisors to focus more on building relationships. Additionally, agents help manage risk by spotting data vulnerabilities.
2. Insurance:
Automation simplifies the claims process from start to finish. AI agents verify claims and gather necessary information. They also interact with customers in a friendly way. This improves efficiency and lets human adjusters handle more complex cases.
Explore the challenges and risks of Agentic AI in What Enterprises Need to Know About Agentic AI Risks.
3. Public Sector:
Government agencies use agentic automation to enhance services for citizens. Tasks like document processing and resource allocation become automated. This approach leads to data-driven decisions, resulting in better public services.
4. Manufacturing:
In factories, predictive maintenance algorithms help prevent machine failures. They reduce downtime effectively. AI also checks product quality and optimizes the supply chain in real-time.
Find out how Agentic AI powers autonomous systems in our blog Building Autonomous Systems from Scratch.
5. Telecommunications:
Agents maintain network reliability by identifying and solving potential problems. This ensures uninterrupted service for customers.
6. Healthcare and Life Sciences:
Agents assist with diagnosing patients and creating tailored treatment plans. They also speed up drug discovery by analyzing large datasets to find promising drug candidates.
Looking to invest in the future of AI? Check out the Top 5 Agentic AI Stocks to watch this January.
7. Customer Experience:
Agentic automation improves customer interactions by offering personalized recommendations and round-the-clock support. AI tools analyze feedback, which helps businesses respond quickly and enhance their offerings.
Discover how Agentic AI is revolutionizing Security Operations Centers in 2025 by reading Transforming SOC Teams in 2025.
8. Employee Experience:
AI agents aid executives in managing employee communications. They summarize feedback and point out necessary actions. This helps ensure timely responses and boosts engagement.
9. Facilities and Equipment Management:
By combining agentic AI with IoT, organizations can monitor and optimize equipment and operations in real-time. This innovation may transform industries like manufacturing and transportation while improving efficiency and safety.
Explore the foundational architecture of Agentic AI systems in Baseline Architecture of Agentic AI Systems.
Overall, agentic automation is growing quickly and offers solutions that improve efficiency, cut costs, and enhance service quality across many sectors.
FAQs About Agentic Automation
1. What does agentic mean in AI?
Agentic AI refers to autonomous systems that can make decisions, learn, and take actions independently to achieve specific goals.
Understand the distinction between LLMs and Agentic AI by reading our in-depth comparison in What is the Difference Between LLM and Agentic AI?.
2. AI Agents vs Agentic AI: What’s the Difference?
AI agents often execute tasks based on programmed rules, while agentic AI incorporates learning and decision-making capabilities to adapt to new situations.
3. What is the difference between RPA and agentic automation?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) handles repetitive, rule-based tasks, while agentic automation uses AI to learn, adapt, and solve complex problems.
4. What is behavioral automation?
Behavioral automation analyzes human actions to predict and influence customer decisions, making marketing strategies more intelligent and personalized.
5. What is an example of an agentic AI?
Autonomous vehicles are a prime example, using AI to make decisions about navigation, routes, and safety in real-time.
6. What is meant by agentic?
Agentic means having the ability to make independent decisions and take actions to achieve a specific goal.
Curious about how Agentic AI differs from traditional AI? Learn about their unique characteristics in our blog Agentic AI vs. Traditional AI.
Final Words
As technology advances, agentic automation is expected to become more widespread. Companies are creating tools to help businesses build and manage smart agents. This shift means more tasks will soon be handled by these intelligent agents. Consequently, we can anticipate greater efficiency and innovation in the workplace.
So, agentic automation marks a major improvement in how we perform tasks. By allowing software agents to make their own decisions, businesses can boost efficiency and cut costs. This change enables them to focus on more important, strategic activities.
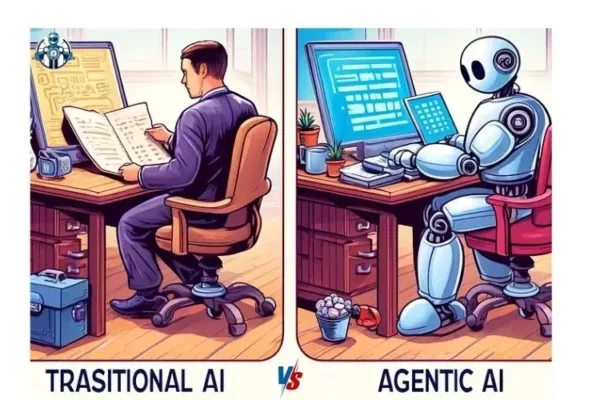










4 thoughts on “Agentic AI vs. Traditional AI: Key Differences and Why It Matters”