When it comes to cybersecurity, social engineering refers to the actions that deceptive attackers take to get authorized users to willingly provide their credentials and other secure data. A social engineering attack is different from a classical hack attack because it does not exploit gaps in programming and system structures but tricks people. It takes considerable time for the attacker to establish rapport and avert the focus away from a specific action that is desirable for the attacker in favor of an action that is the least desirable for the victim.
What is the Psychology behind Social Engineering?
Actually, social engineering is based on people’s tendency and takes advantage of their confidence, fear and the feeling of the urgency. Usually, the attackers design circumstances that make the victims comfortable or compelled to respond rapidly. This is something that makes social engineering very efficient.
What is the impact of Social Engineering on organizations?
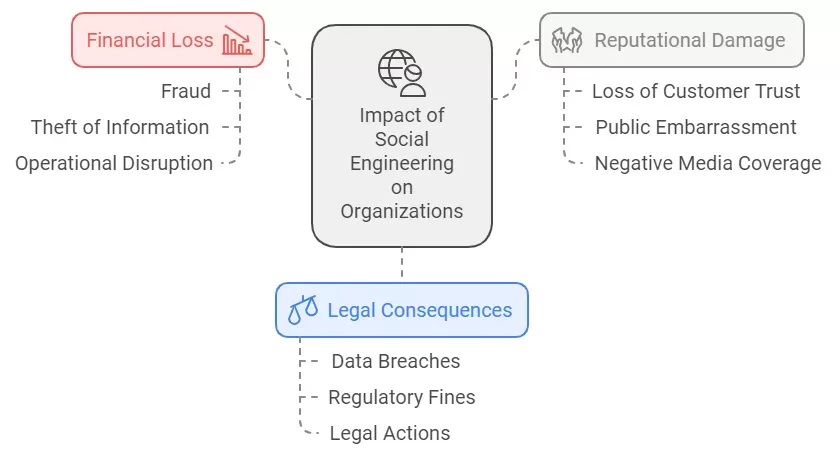
Social engineering can have severe consequences for organizations, including:
· Financial Loss:
An attack may be financially rewarding if it brings about fraud or theft of valuable information and thus becoming financially productive.
· Reputational Damage:
An organization which has suffered an attack loses the trust of its customer and maybe subject to public embarrassment.
· Legal Consequences:
Data breaches leads to so many legal actions and regulatory fines in the event of field data breaches.
Curious about how social engineers manipulate their targets? Read how does social engineering work? to learn how these tactics work and how to defend against them!
What makes social engineering so different from traditional hacking

Social engineering and hacking are two different ways of attacking security though they have their similarities and differences as will be seen below. The understanding of those differences is an essential prerequisite to the realization of sufficient cybersecurity.
- Approach to Compromise
Social Engineering:
This method is based on the inclination arising in people’s mind to take an action. Social engineering leverages human trust, feelings, and relationships with other people to force them into revealing confidential data or make wrong actions. For example, they may pose as a familiar coworker or use fear and pressure to make you reply more quickly.
Traditional Hacking:
As for the traditional hacking it is oriented on using of some program or system misfeatures. Criminals utilize tools and methods to avoid protection mechanisms, and penetrate a system by taking advantage of the inherent vulnerabilities in the software or introducing malicious programs.
- Techniques Used
Social Engineering Techniques:
Phishing: Sending fraudulent emails that appear legitimate.
Vishing: Using phone calls to impersonate trusted figures.
Baiting: Offering enticing rewards to lure victims into providing information.
Traditional Hacking Techniques:

Malware: Installing malicious software to gain access or steal data.
SQL Injection: Exploiting vulnerabilities in databases to manipulate data.
Brute Force Attacks: Attempting multiple passwords until the correct one is found.
- Target Focus
Social Engineering: Targets individuals within an organization. The success of these attacks often hinges on the attacker’s ability to build rapport and trust with the victim.
Traditional Hacking: Targets systems and networks rather than individuals. The focus is on finding weaknesses in technology rather than exploiting human behavior.
- Detection and Prevention
Social Engineering Prevention:
- Conduct regular training for employees on recognizing social engineering tactics.
- Implement verification protocols for requests involving sensitive information.
Traditional Hacking Prevention:
- Use firewalls and antivirus software to protect systems.
- Regularly update software to patch vulnerabilities.
How does human error contribute to social engineering?
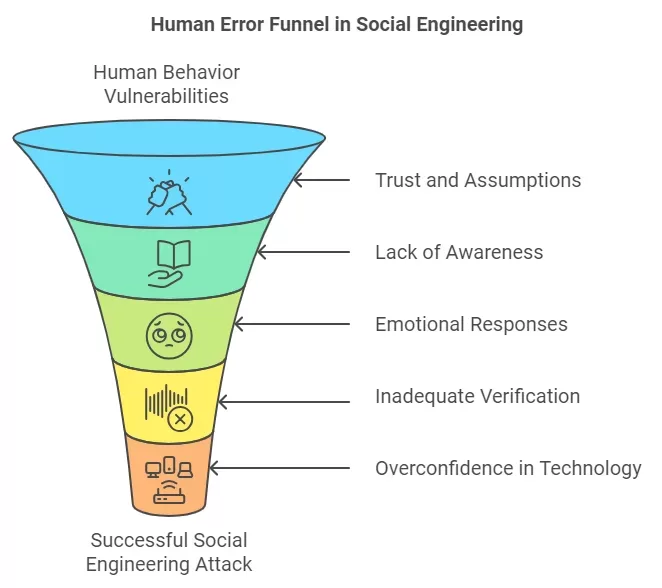
Human error significantly contributes to the success of social engineering attacks, as attackers exploit vulnerabilities in human behavior rather than technical systems. Here’s how human error plays a crucial role in facilitating these deceptive tactics:
- Trust and Assumptions
People naturally tend to trust others, especially those who appear familiar or authoritative. This trust can lead to errors in judgment, causing individuals to share sensitive information without verifying the request.
For example, an employee might receive a seemingly legitimate email from someone posing as their IT department and unwittingly provide login credentials.
- Lack of Awareness
Many individuals are unaware of the various social engineering tactics used by attackers. Without proper training, employees may not recognize the signs of phishing emails or suspicious phone calls. This lack of awareness can lead to mistakes, such as clicking on malicious links or downloading infected attachments.
- Emotional Responses
Social engineers often exploit emotions like fear, urgency, or curiosity to manipulate their targets. For instance, an urgent request for action may prompt someone to act quickly without considering the legitimacy of the request. This emotional manipulation can lead to hasty decisions that compromise security.
- Inadequate Verification Processes
When individuals do not follow proper verification protocols, they increase their susceptibility to social engineering attacks.
For example, if an employee receives a request for sensitive information via email but does not take the time to verify the sender’s identity through a separate communication channel. They may inadvertently expose their organization’s data.
- Overconfidence in Technology
Some individuals may have an overreliance on technology and believe that security measures alone are sufficient to protect against threats. This mindset can lead to complacency and a lack of vigilance when it comes to recognizing social engineering attempts.
How can cybersecurity awareness stop social engineering?

Cybersecurity awareness is crucial in combating social engineering attacks. By educating individuals about the tactics used by attackers, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to manipulation. Here’s how awareness can help:
- Recognizing Tactics
Awareness training enables individuals to identify common social engineering techniques, such as phishing, vishing, and baiting. Understanding these tactics helps employees recognize suspicious communications and avoid making costly mistakes.
2. Building a Culture of Skepticism
Promoting a culture of skepticism encourages employees to question unexpected requests for sensitive information. When individuals are trained to verify requests through separate channels, they are less likely to be deceived.
3. Empowering Employees
Training empowers employees with the knowledge and tools needed to respond effectively to potential threats. When staff feel confident in their ability to recognize and report suspicious activity, they become a strong line of defense against social engineering.
4. Implementing Strong Security Practices
Awareness programs often emphasize the importance of security practices, such as using multi-factor authentication and regularly updating passwords. These measures add layers of protection that make it harder for attackers to succeed.
Final Words
Cybersecurity awareness is a powerful tool in the fight against social engineering. By educating individuals and fostering a culture of vigilance, organizations can better protect themselves from these deceptive tactics. For more in-depth insights on social engineering and how to enhance your cybersecurity posture, check out our ultimate pillar page ”What is Social Engineering and How Does It Work?”